Do you own an iPhone? Mac? Or any Apple device?
Just one specially-crafted message can expose your personal information, including your authentication credentials stored in your device’s memory, to a hacker.
The vulnerability is quite similar to the Stagefright vulnerabilities, discovered a year ago in Android, that allowed hackers to silently spy on almost a Billion phones with just one specially-crafted text message.
Cisco Talos senior researcher Tyler Bohan, who discovered this critical Stagefright-type bug in iOS, described the flaw as “an extremely critical bug, comparable to the Android Stagefright as far as exposure goes.”
The critical bug (CVE-2016-4631) actually resides in ImageIO – API used to handle image data – and works across all widely-used Apple operating systems, including Mac OS X, tvOS, and watchOS.
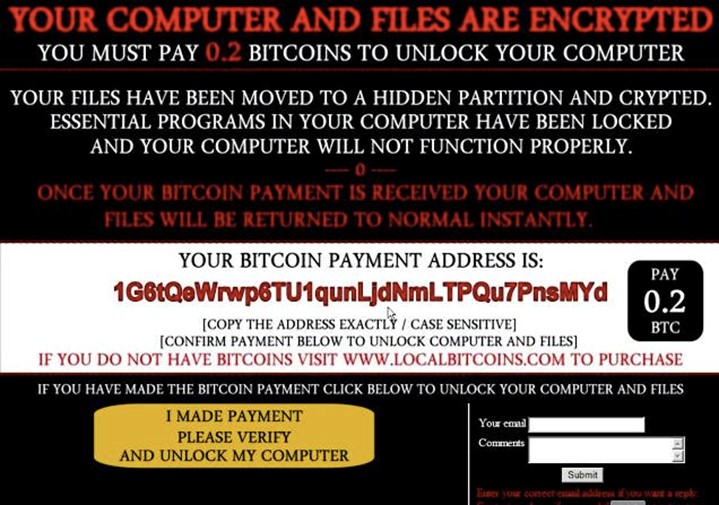
All an attacker needs to do is create an exploit for the bug and send it via a multimedia message (MMS) or iMessage inside a Tagged Image File Format (TIFF).
Once the message received on the victim’s device, the hack would launch.
“The receiver of an MMS cannot prevent exploitation and MMS is a store and deliver mechanism, so I can send the exploit today and you will receive it whenever your phone is online,” Bohan quoted as saying by Forbes.
The attack could also be delivered through Safari web browser. For this, the attacker needs to trick the victim into visiting a website that contains the malicious payload.
In both the cases, no explicit user interaction would be required to launch the attack since many applications (like iMessage) automatically attempt to render images when they are received in their default configurations.
It is quite difficult for the victim to detect the attack, which if executed, could leak victims’ authentication credentials stored in memory such as Wi-Fi passwords, website credentials, and email logins, to the attacker.
Since iOS include sandbox protection to prevent hackers exploiting one part of the OS to control the whole thing, a hacker would require a further iOS jailbreak or root exploit to take total control of the complete iPhone.
However, Mac OS X does not have sandbox protection that could allow an attacker to access the Mac computer remotely with the victim’s passwords, potentially making users of Apple’s PCs completely vulnerable to the attack.
Apple has patched this critical issue in iOS version 9.3.3, along with patches for other 42 vulnerabilities, including memory corruption bugs in iOS’ CoreGraphics that helps render 2D graphics across those OSes, according to Apple’s advisory.
Apple also addressed serious security vulnerabilities in FaceTime on both iOS and OS X platforms, allowing anyone on the same WiFi network as a user to eavesdrop on the audio transmission from FaceTime calls even after the user had ended the call.
“An attacker in a privileged network position [could] cause a relayed call to continue transmitting audio while appearing as if the call terminated,” reads Apple description.
The FaceTime vulnerability (CVE-2016-4635) was discovered and reported by Martin Vigo, a security engineer at Salesforce.
So users are advised to patch their devices as it would not take enough time for bad actors to take advantage of the vulnerabilities, which are now known.
Via: thehackernews