When it comes to the technical aspects of PCI DSS, HIPAA, SOX, and other regulatory frameworks, the goals are often the same: to protect the privacy and security of sensitive data. But the motivators for businesses to comply with these regulatory schemes varies greatly.
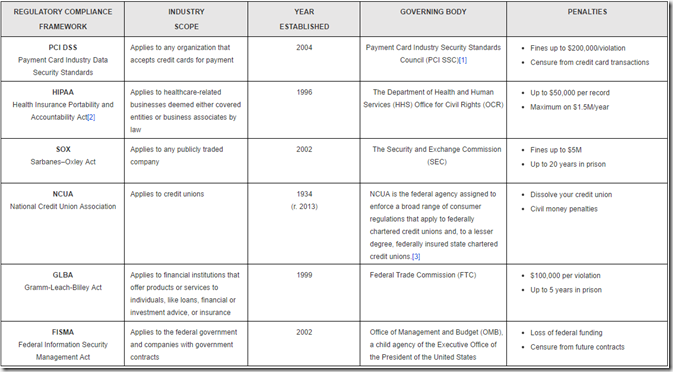
This list only represents a fraction of the entire regulatory compliance structures that govern the use of information technology and processes involved in maintaining the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of sensitive data of all types.
Yes, there are monetary fines for noncompliance or unlawful uses or disclosures of sensitive information – the chart above provides an overview of that – and for most, that alone offers plenty of incentive to comply. But beyond this, businesses should be aware of the many other consequences that can result from non-compliance or any other form of negligence that results in a breach.
INDIRECT CONSEQUENCES OF NONCOMPLIANCE
Noncompliance whether validated by audits, or discovered as the result of a breach, can be devastating for a business. Though, when a breach occurs, its impact often extends well beyond the fines and penalties levied by enforcement agencies. It can include the cost of detecting the root cause of a breach, remediating it, and notifying those affected. Further, the cost balloons when you factor in legal expenditures, business-related expenses, and loss of revenues faced by damaged brand reputation.
As if IT pros did not have enough to worry about these days, yes, unfortunately compliance too falls into their laps. But depending on the industries they serve and the types of data their business interacts with, what compliance actually entails can be quite different.
REGULATORY COMPLIANCE AND THE INTERSECTION WITH IT
Without a doubt, there are many aspects of data security standards and compliance regulations that overshadow everything from IT decision-making and purchasing, to configurations, and the policies and procedures a company must create and enforce to uphold this important task.
Organizations looking to comply with a particular regulatory framework must understand that no one solution, and no one vendor, can help prepare them for all aspects of compliance. It is important that IT professionals understand the objectives of every compliance framework they are subject to, and plan accordingly.
[1] The PCI SSC was founded by American Express, Discover Financial Services, JCB International, MasterCard Worldwide and Visa Inc. Participating organizations include merchants, payment card-issuing banks, processors, developers, and other vendors.
[2] The Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health (HITECH) Act, which was enacted as part of the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009, prompted the adoption of Health Information Technology. This act is recognized as giving “teeth” to HIPAA as it established stricter requirements by establishing the Privacy, Security, and Breach Notification Rules, as well as stiffer penalties for violations. The HIPAA Omnibus Rule, which went into effect in 2013, further strengthened the OCR’s ability to enforce compliance, and clearly defined the responsibility of compliance for all parties that interact with electronic protected health information (ePHI).
[3] It is important to note that in the financial world, guidance from the Federal Financial Institute of Examiners Council (FFIEC) to a bank is mandatory because the guidance specifies the standards that the examiner will use to evaluate the bank. Credit unions technically fall under a different regulator than banks, however, the National Credit Union Association closely follows the FFIEC guidance.
via: solarwinds



